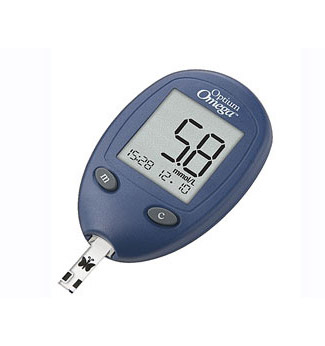
a group of endocrine diseases associated with impaired glucose uptake due to absolute or relative (impaired interaction with target cells) insufficiency of the hormone insulin. As a result, hyperglycemia develops — a persistent increase in blood glucose. The disease is characterized by a chronic course, as well as a violation of all types of metabolism: carbohydrate, fat, protein, mineral and water-salt[3][4]. In addition to humans, some animals, such as cats and dogs, are also susceptible to this disease[5].